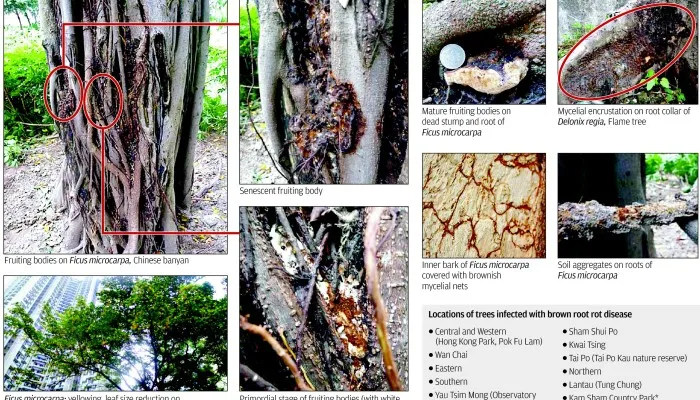
Brown Root Rot Disease is caused by the fungus Phellinus noxius. The fungus attacks tree roots causing decay. This cuts off water and nutrient supply to the crown, causing tree death. Occurring naturally in rainforests, the disease has become a problem in forest plantations, fruit orchards and urban environments. BRRD is caused by the aggressive fungal pathogen Phellinus noxius, a white rot fungus that could result in rapid health and structural deterioration of trees.
Comprehensive Guide to Brown Root Rot Disease (BRRD)
Root diseases, including root rot, occur when soil-borne pathogens, such as fungi, infect plant roots. Excess moisture is a primary culprit, creating an environment conducive to diseases like Phytophthora or Pythium. Symptoms include discolored, mushy roots and stunted plant growth. Crops like soybeans and ornamental plants like orchids often suffer from brown orchid roots or brown stem rot, which can significantly reduce yield and plant health.
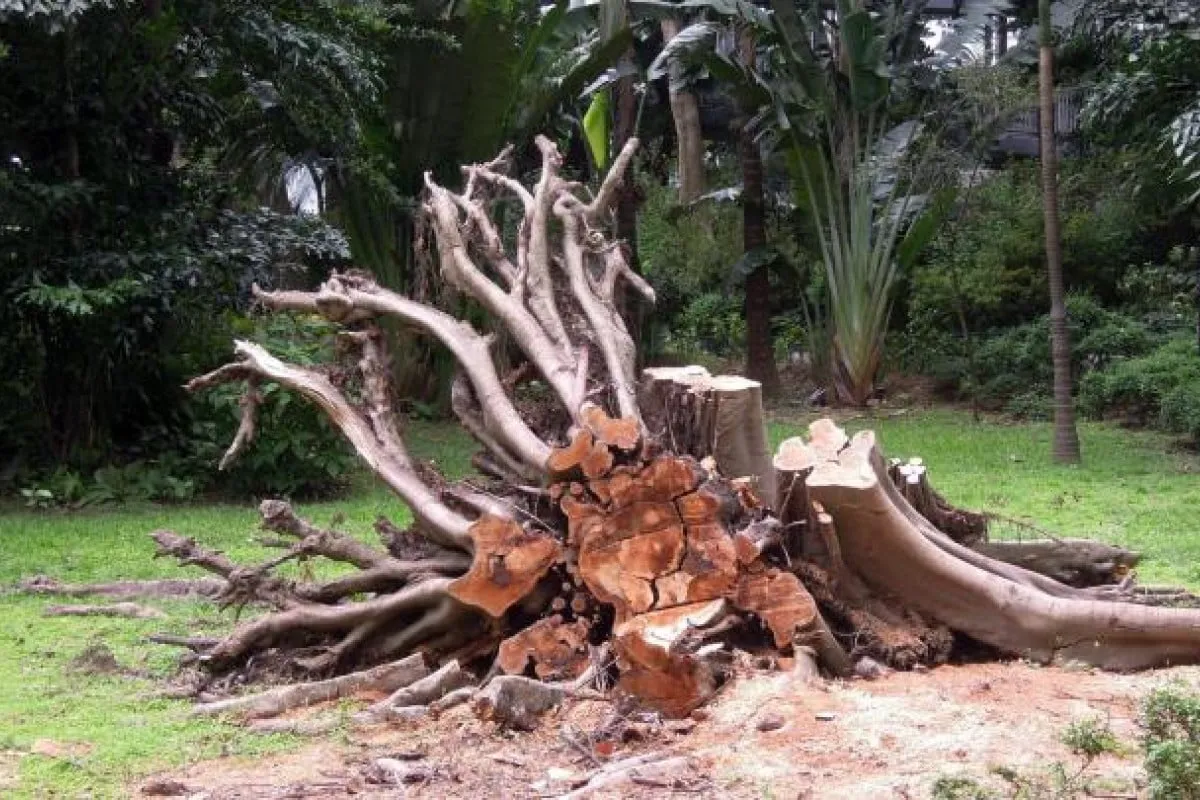

Brown root rot disease (BRRD) is a highly destructive tree disease. Early diagnosis of BRRD has been challenging because the first symptoms and signs are often observed after extensive tissue colonization. Brown root rot is a disease of woody plants that causes decline and death of trees throughout the tropics. The name brown root rot refers to a dark brown crust formed by the fungus, Phellinus noxius (Corner) Cunningham, on exposed roots and lower plant stems.
Comprehensive Overview of Plant Diseases and Related Problems
Plant diseases can severely affect the health and appearance of vegetation, from lawns and crops to ornamental plants and trees. These diseases often result from fungal, bacterial, or viral infections, as well as environmental stressors. Understanding common issues like root disease, lawn disease, and specific plant afflictions is essential for diagnosis and treatment.
Lawn Diseases: Brown Spots and Brown Patch
Lawn diseases are a common concern for homeowners, often manifesting as brown spots, patches, or areas of thinning grass. Brown patch lawn disease, caused by the fungus Rhizoctonia solani, is especially prevalent in warm, humid conditions. Similarly, large patch disease affects warm-season grasses like St. Augustine and Bermuda, creating circular areas of discolored turf. Diagnosing these problems early is key to lawn recovery.
Fungal Diseases in Plants
Fungal pathogens are among the most damaging to plants, causing issues like crown rot, tree disease, and leaf blight. Fungi can attack various parts of the plant, leading to symptoms like brown leaves, defoliation, or the formation of cankers. Infections such as orchid disease or sesame disease can significantly harm both ornamental and agricultural species, requiring targeted fungicides for treatment.
Crop-Specific Concerns: Soybean and Sesame Diseases
Agricultural crops are not immune to diseases. Soybean disease and sesame disease often result from fungal infections, which thrive in poorly drained fields. Brown stem rot, for instance, causes wilting and discoloration of stems and leaves, leading to significant yield losses. Phellinus noxius is a fungus that causes the disease brown root rot in trees. It attacks tree roots causing decay, which cuts off water and nutrient supply to the crown resulting in tree death.
Signs and Identification of Grass and Turf Diseases
To answer questions like “How do I identify a grass disease?” or “What does turf disease look like?” gardeners should watch for irregularly shaped patches of discolored grass, wilting blades, or the presence of fungal growth. Conditions like lawn fungus and disease may also attract secondary problems like insects and diseases that further compromise turf health.
Conclusion Brown Root Rot Disease
Brown root rot disease poses a major challenge to plant health, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. Preventive measures, early detection, and integrated management practices are key to minimizing its impact. With continued research, sustainable solutions can be developed to protect both crops and ecosystems. Brown Root Rot Disease (BRRD) is one of the most devastating urban tree diseases in tropical and subtropical areas, including Hong Kong. It can result in tree death in a few months and is difficult to detect in the early stages of development.
